A chart is a visual representation of numeric values. Charts (also known as graphs) have been an integral part of spreadsheets. Charts generated by early spreadsheet products were quite crude, but thy have improved significantly over the years. Excel provides you with the tools to create a wide variety of highly customizable charts. Displaying data in a well-conceived chart can make your numbers more understandable. Because a chart presents a picture, charts are particularly useful for summarizing a series of numbers and their interrelationships.
Types of Charts
There are various chart types available in MS Excel as shown in the below screen-shot: Column − Column chart shows data changes over a period of time or illustrates comparisons among items.
Bar − A bar chart illustrates comparisons among individual items.
Pie − A pie chart shows the size of items that make up a data series, proportional to the sum of the items. It always shows only one data series and is useful when you want to emphasize a significant element in the data.
Line − A line chart shows trends in data at equal intervals.
Area − An area chart emphasizes the magnitude of change over time.
X Y Scatter − An xy (scatter) chart shows the relationships among the numeric values in several data series, or plots two groups of numbers as one series of xy coordinates.
Stock − This chart type is most often used for stock price data, but can also be used for scientific data (for example, to indicate temperature changes).
Surface − A surface chart is useful when you want to find the optimum combinations between two sets of data. As in a topographic map, colors and patterns indicate areas that are in the same range of values.
Doughnut − Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole; however, it can contain more than one data series.
Bubble − Data that is arranged in columns on a worksheet, so that x values are listed in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values are listed in adjacent columns, can be plotted in a bubble chart.
Radar − A radar chart compares the aggregate values of a number of data series.
Creating Chart
To create charts for the data by below mentioned steps.
Select the data for which you want to create the chart.
Choose Insert Tab » Select the chart or click on the Chart group to see various chart types.
Select the chart of your choice and click OK to generate the chart.
Editing Chart
You can edit the chart at any time after you have created it.
You can select the different data for chart input with Right click on chart » Select data. Selecting new data will generate the chart as per the new data, as shown in the below screen-shot:
You can change the X axis of the chart by giving different inputs to X-axis of chart.
You can change the Y axis of chart by giving different inputs to Y-axis of chart.
Pivot Charts
A pivot chart is a graphical representation of a data summary, displayed in a pivot table. A pivot chart is always based on a pivot table.
Although Excel lets you create a pivot table and a pivot chart at the same time, you can’t create a pivot chart without a pivot table. All Excel charting features are available in a pivot chart.
Pivot charts are available under Insert tab » PivotTable dropdown » PivotChart.
Pivot Chart Example
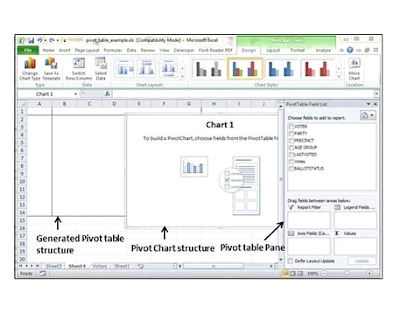
Now, let us see Pivot table with the help of an example. Suppose you have huge data of voters and you want to see the summarized view of the data of voter Information per party in the form of charts, then you can use the Pivot chart for it. Choose Insert tab » Pivot Chart to insert the pivot table.
Microsoft Excel selects the data of the table. You can select the pivot chart location as an existing sheet or a new sheet. Pivot chart depends on automatically created pivot table by the MS Excel. You can generate the pivot chart in the below screen-shot.
Types of Charts
There are various chart types available in MS Excel as shown in the below screen-shot: Column − Column chart shows data changes over a period of time or illustrates comparisons among items.
Bar − A bar chart illustrates comparisons among individual items.
Pie − A pie chart shows the size of items that make up a data series, proportional to the sum of the items. It always shows only one data series and is useful when you want to emphasize a significant element in the data.
Line − A line chart shows trends in data at equal intervals.
Area − An area chart emphasizes the magnitude of change over time.
X Y Scatter − An xy (scatter) chart shows the relationships among the numeric values in several data series, or plots two groups of numbers as one series of xy coordinates.
Stock − This chart type is most often used for stock price data, but can also be used for scientific data (for example, to indicate temperature changes).
Surface − A surface chart is useful when you want to find the optimum combinations between two sets of data. As in a topographic map, colors and patterns indicate areas that are in the same range of values.
Doughnut − Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole; however, it can contain more than one data series.
Bubble − Data that is arranged in columns on a worksheet, so that x values are listed in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values are listed in adjacent columns, can be plotted in a bubble chart.
Radar − A radar chart compares the aggregate values of a number of data series.
Creating Chart
To create charts for the data by below mentioned steps.
Select the data for which you want to create the chart.
Choose Insert Tab » Select the chart or click on the Chart group to see various chart types.
Select the chart of your choice and click OK to generate the chart.
Editing Chart
You can edit the chart at any time after you have created it.
You can select the different data for chart input with Right click on chart » Select data. Selecting new data will generate the chart as per the new data, as shown in the below screen-shot:
You can change the X axis of the chart by giving different inputs to X-axis of chart.
You can change the Y axis of chart by giving different inputs to Y-axis of chart.
Pivot Charts
A pivot chart is a graphical representation of a data summary, displayed in a pivot table. A pivot chart is always based on a pivot table.
Although Excel lets you create a pivot table and a pivot chart at the same time, you can’t create a pivot chart without a pivot table. All Excel charting features are available in a pivot chart.
Pivot charts are available under Insert tab » PivotTable dropdown » PivotChart.
Pivot Chart Example
Now, let us see Pivot table with the help of an example. Suppose you have huge data of voters and you want to see the summarized view of the data of voter Information per party in the form of charts, then you can use the Pivot chart for it. Choose Insert tab » Pivot Chart to insert the pivot table.
Microsoft Excel selects the data of the table. You can select the pivot chart location as an existing sheet or a new sheet. Pivot chart depends on automatically created pivot table by the MS Excel. You can generate the pivot chart in the below screen-shot.









0 Comments